As the world’s digital economy continues to grow and mature, digital infrastructure has become a key driver and enabler underpinning economic development. Along with computing power and network connectivity, efficient and reliable data storage is a cornerstone of effective digital infrastructure.
By 2030, the world is expected to enter the yottabyte era, dealing regularly with data quantities on the scale of a quadrillion gigabytes. Working with such data will place huge demands on storage capacity and require optimised storage functions to read, write, and transmit data efficiently and reliably. As such, data storage power rises in importance as it used to assess the potential effectiveness of data storage systems as a crucial element of modern digital infrastructure.
Evaluating data storage power with the MEGA framework
Data storage power comprises four dimensions: storage capacity (how much data the system can hold), performance (what the system can do), reliability (can the system keep data intact and available), and greenness (how low the system’s carbon footprint is).
 Huawei
HuaweiEvaluating relative data storage power can be achieved through the four dimensions of the MEGA indicator system, which offers meaningful measurement to allow comparison and ranking for assessment.
- Magnitude refers to Adequacy, measuring the magnitude of storage capacity, and Momentum, measuring the growth of investment in storage capacity.
- Efficiency refers to Balance, the correlation of computing and storage power to the overall efficiency of digital infrastructure, and Agility, measuring the proportion of high-performance flash memory in the system.
- Groundwork refers to the reliability of the system, in terms of its ability to prevent data loss and recover quickly after a disruption.
- Advancement refers to Greenness, which focuses on energy efficiency and environmental impact, and Cutting-Edge, reflecting efforts to develop and incorporate technical research and new technologies.
The MEGA framework is applicable from macro to micro scales and can be adapted for assessments at various levels, from regional development to individual storage devices, with relevant adjustment of the factors measured.
Understanding its value and impact
Data storage is recognised as a significant contributor to economic development, in the form of direct, indirect, and induced economic contributions. The direct impact of data storage development, measured as the immediate economic and social value arising from data storage development, is estimated to bring US$5 into the local economy for every US$1 invested in data storage.
Indirect impact, which counts the value of subsequent data-production activities such as data processing, is estimated to contribute up to US$8 per US$1 invested. Induced impact, which takes into account data storage’s enhancement of government management, enterprise services, and public livelihood, is assessed to produce US$40 for every US$1 invested.
Recognising the economic and social potential of data storage power, there is a need for an indicator system to analyse data storage power at the macroeconomic level. The MEGA framework can be applied using the dimensions for regional development. For example, Huawei applied the framework to a survey of 20 countries:
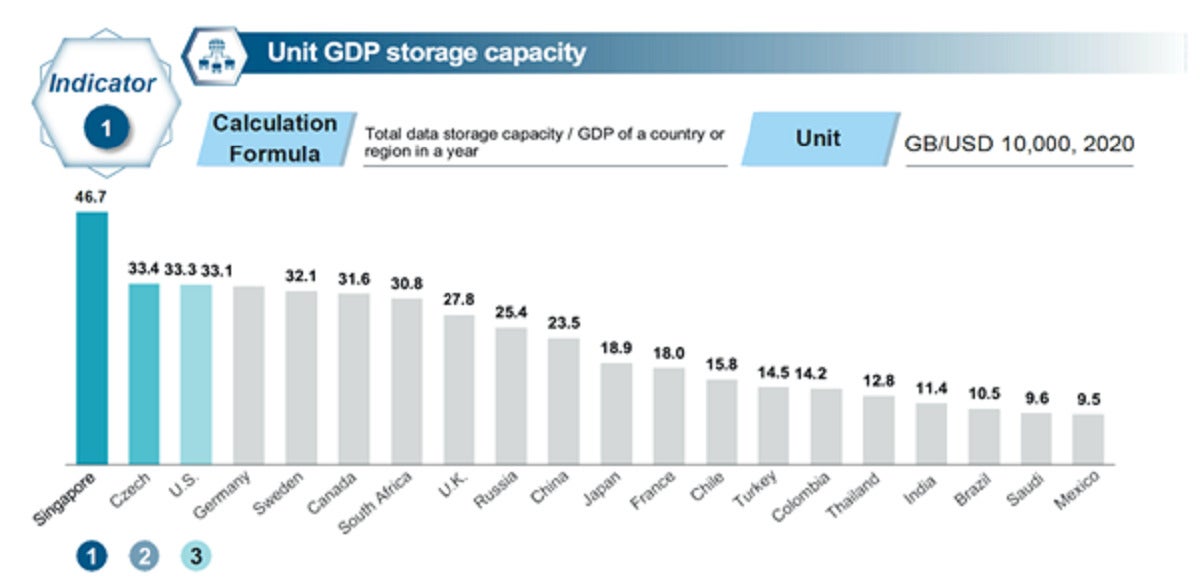
- Magnitude. Storage Capacity Per Unit GDP measures the capacity of data storage devices per current year’s regional GDP. Among the 20 countries measured, Singapore emerged first.
 Huawei
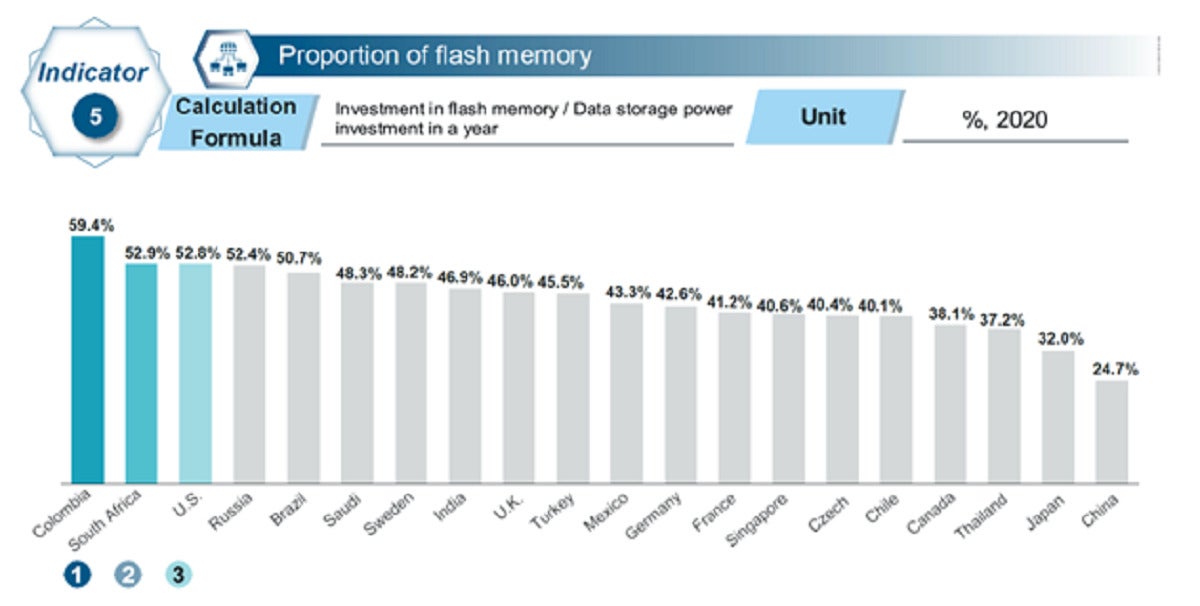
Huawei- Efficiency. Measuring the proportion of Flash Storage investment relative to all data storage investment provides an indication of the agility and future-readiness of the region’s data storage. Colombia is at the top of this ranking.
 Huawei
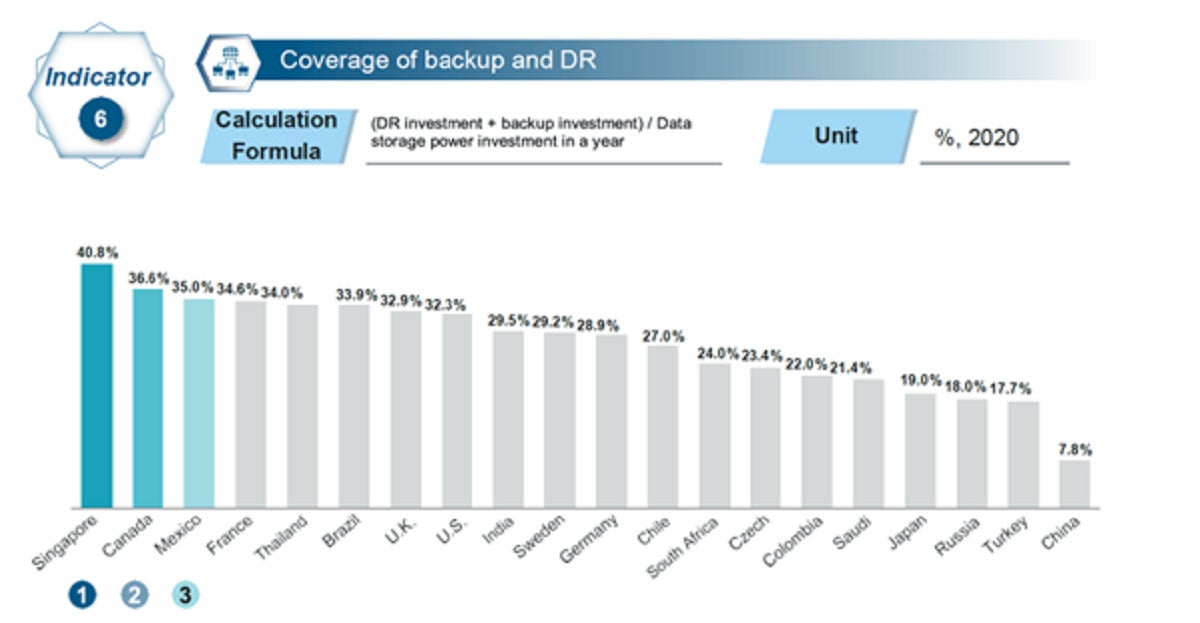
Huawei- Groundwork. Storage reliability, covering backup and disaster recovery (DR), is an important indicator of a system’s ability to react and recover quickly from disruptions such as attacks and natural disasters. Singapore claimed the top ranking in terms of investment in backup and DR capability.
 Huawei
HuaweiWhat the future holds for data storage power
Data storage has a crucial role to play in building digital infrastructure to meet tomorrow’s diverse digital workloads and power the digital economy.
To move forward meaningfully, the government must foster a conducive environment. This could come in the form of policies, support programs, and planning—be it supporting the development of associated data infrastructure areas, building high-tech zones or technology parks that cultivate deeper innovation, or data protection laws.
It’s also important for the government to catalyse the private sector to drive storage power development. Today’s market is not fully aware of the importance of storage power, causing its deprioritisation. To drive market awareness of data storage power, governments can lead by example through initiatives such as developing government clouds and smart cities, focusing on efficiency, green, and security while constructing data storage power and data centre infrastructure.
Deep dive into why data storage power is the digital cornerstone of high-quality social development and how to build them here.
Under the theme “Unleash Digital”, Huawei Connect 2022 will also take place in Shenzhen starting from Nov 7. The annual event will introduce a number of ICT products, portfolios, and solutions designed to meet the needs of various industry scenarios. Through a series of summits, broadcasts and exhibitions, we will also give a sneak peek at new groundbreaking innovations, as well as best practices and results from Huawei’s work with customers and partners around the world.






